The Windows Registry 8
Using the Registry: Program Examples
The following sample code demonstrates how to use the registry functions.
- Enumerating Registry Subkeys Program Example
- Creating the Registry Subkey and Value Program Example
- Deleting Registry Key with Subkeys Program Example
- Determining the Registry Size Program Example
- Querying the Registry Value Program Example
Enumerating Registry Subkeys Program Example
The following example uses the RegQueryInfoKey(), RegEnumKeyEx(), and RegEnumValue() functions to enumerate the subkeys of the specified key. The hKey parameter passed to each function is a handle to an open key. This key must be opened before the function call and closed afterward. Create a new empty Win32 console application project. Give a suitable project name and change the project location if needed.
Then, add the source file and give it a suitable name.
Next, add the following source code.
// QueryKey - Enumerates the subkeys of key and its associated values.
// hKey - Key whose subkeys and values are to be enumerated.
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_KEY_LENGTH 255
#define MAX_VALUE_NAME 16383
void QueryKey(HKEY hKey)
{
WCHAR achKey[MAX_KEY_LENGTH]; // buffer for subkey name
DWORD cbName; // size of name string
WCHAR achClass[MAX_PATH] = TEXT(); // buffer for class name
DWORD cchClassName = MAX_PATH; // size of class string
DWORD cSubKeys=0; // number of subkeys
DWORD cbMaxSubKey; // longest subkey size
DWORD cchMaxClass; // longest class string
DWORD cValues; // number of values for key
DWORD cchMaxValue; // longest value name
DWORD cbMaxValueData; // longest value data
DWORD cbSecurityDescriptor; // size of security descriptor
FILETIME ftLastWriteTime; // last write time
DWORD i, retCode;
WCHAR achValue[MAX_VALUE_NAME];
DWORD cchValue = MAX_VALUE_NAME;
// Get the class name and the value count.
retCode = RegQueryInfoKey(
hKey, // key handle
achClass, // buffer for class name
&cchClassName, // size of class string
NULL, // reserved
&cSubKeys, // number of subkeys
&cbMaxSubKey, // longest subkey size
&cchMaxClass, // longest class string
&cValues, // number of values for this key
&cchMaxValue, // longest value name
&cbMaxValueData, // longest value data
&cbSecurityDescriptor, // security descriptor
&ftLastWriteTime); // last write time
wprintf(LRegQueryInfoKey() returns %u\n, retCode);
// Enumerate the subkeys, until RegEnumKeyEx() fails
if (cSubKeys)
{
wprintf(L\nNumber of subkeys: %d\n, cSubKeys);
for (i=0; i<cSubKeys; i++)
{
cbName = MAX_KEY_LENGTH;
retCode = RegEnumKeyEx(hKey, i,achKey,&cbName,NULL,NULL,NULL,&ftLastWriteTime);
if (retCode == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(L(%d) %s\n, i+1, achKey);
}
}
}
else
wprintf(LNo subkeys to be enumerated!\n);
// Enumerate the key values
if (cValues)
{
wprintf(L\nNumber of values: %d\n, cValues);
for (i=0, retCode=ERROR_SUCCESS; i<cValues; i++)
{
cchValue = MAX_VALUE_NAME;
achValue[0] = '\0';
retCode = RegEnumValue(hKey, i, achValue, &cchValue, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (retCode == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(L(%d) %s\n, i+1, achValue);
}
}
}
else
wprintf(LNo values to be enumerated!\n);
}
int wmain(int argc, WCHAR *argv[])
{
HKEY hTestKey;
// Change the key and subkey accordingly...
// In this case: HKEY_USERS\\S-1-5-18\\...
if(RegOpenKeyEx(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, LSYSTEM\\Setup /*LS-1-5-18*/, 0, KEY_READ, &hTestKey) == ERROR_SUCCESS)
// if(RegOpenKeyEx(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, LSYSTEM\\WPA, 0, KEY_READ, &hTestKey) == ERROR_SUCCESS)
{
wprintf(LRegOpenKeyEx() is OK! Registry key is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\\Setup...\n);
QueryKey(hTestKey);
}
else
wprintf(LRegOpenKeyEx() failed!\n);
if(RegCloseKey(hTestKey) == ERROR_SUCCESS)
wprintf(LhTestKey key was closed successfully!\n);
else
wprintf(LFail to close hTestKey key!\n);
return 0;
}
Build and run the project. The following screenshot is a sample output.
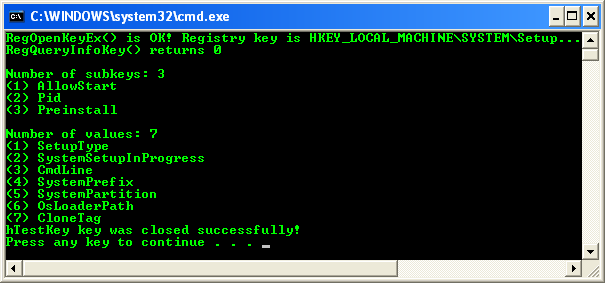
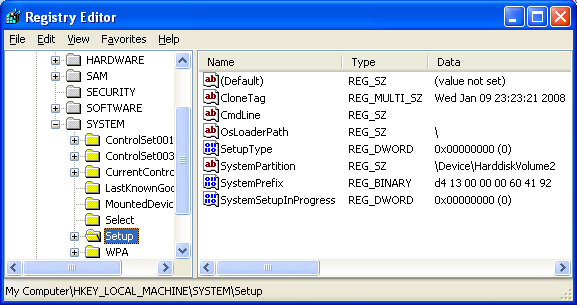
Verify the result against the real registry keys.
< Windows Registry 7 | Windows Registry Index | Win32 Programming | Windows Registry 9 >